In the world of data, it can be challenging to stay abreast of the lightning-fast evolution as yesterday’s burning concern (data compliance) gives way to today’s most urgent priority (ChatGPT). In recent years companies have come to realize data as its own layer of the tech stack—and its value is paramount to the firm. It’s also increasingly clear that not all data is created equal.
In raw form, data is of limited value. Only high-quality data—demonstrating accuracy, consistency, validity, completeness, uniqueness, and integrity—engenders the levels of trust end-users will rely on to evaluate customer needs, engage in meaningful interactions, and close deals that drive enterprise growth.
We know financial services firms invest—heavily—in efforts to improve data quality by:
- Capturing data gathered in the platforms users rely on every day, migrating it from one platform (think email) and sharing it with others (think CRM) and vice versa;
- Implementing processes and protocols to control the way data is captured, reducing the incidence of duplication, omission, and errors;
- Governing access to and use of captured data to ensure compliance and security; and
- Distributing good data where and when it’s needed.
While these efforts have significantly moved the data quality dial in the right direction, there is still more that can be done as your data makes its way through the enterprise. Today’s forward-thinking enterprises leverage data observability to engage end-users to monitor and improve the data on which they rely.
What is Data Observability?
In the simplest terms, data observability refers to an enterprise’s ability to monitor data along its lifecycle.
By empowering admins and end-users with data observability tools enterprises improve their ability to attain the best, most meaningful, and most trustworthy data possible.
From the moment customer or revenue data is gathered via CRM, email, calendar, contacts, chat, etc. – effective data observability allows end-users to see it, manage it, pinpoint issues with the data to improve and ensure its high level of quality and relevance
Data observability tools help IT and operations stakeholders to better understand, govern, and leverage customer data throughout its full and renewing lifecycle. Like end-users, admins have a vested interest in data quality, but from a systems and process perspective, with concerns about data flow, distribution, security, and compliance. When IT and operations teams can keep tabs on the data’s journey through the enterprise, they’re empowered to intervene early—before inconsistencies and substandard use patterns can taint the quality of the data end-users receive.
When embraced as a practice, data observability allows an enterprise to evaluate data throughout its lifetime for:
- Freshness
Data’s value is often directly correlated to its recency and relevancy. Data observability tools help organizations confirm that data is up-to-date—and that it’s being updated over time to ensure relevance and timeliness as it migrates throughout the enterprise. - Distribution
Outlying data values can result from unusual circumstances. They can also signify inaccuracies and process/capture issues that can go unnoticed. Data observability tools allow the enterprise to automatically surface, verify, and, if necessary, resolve unexpected variations before they adversely impact data quality. - Volume
By raising red flags when data assets are incomplete (e.g., do they contain the correct number of rows and columns?), data observancy tools trigger closer evaluation to isolate discrepancies and investigate their root causes. Monitoring data volume creates higher data quality for end-users and helps to ensure the consistency of data intake and transfer efforts—ultimately preventing downstream data quality issues. - Schema
Auditing changes to data tables is a critical piece of data hygiene. With forward-thinking approaches to data observability, changes are highlighted—potentially revealing broken data that can lead to data compromise or lost access to critical data points. - Lineage
This measure helps enterprises to authenticate data provenance by revealing upstream data sources, downstream targets, and a clearer picture of who interacts with the data in its development—and when. Insights on data lineage can help teams quickly identify the root of data anomalies and to resolve them.
How Data Observability Prevents Small Data Issues Before They Grow

One of the most profound advantages of data observability is its capacity to isolate and resolve issues early—at any point in the data lifecycle. This helps enterprises to avoid the “broken window” phenomenon—a concept borrowed from criminal law highlighting the importance of tackling minor problems (e.g., a broken window in a vacant building) before they invite follow-on behavior that ultimately leads to more severe misbehavior (e.g., widespread vandalism).
Following its introduction among criminal law academics, technologists co-opted Broken Window Theory to illustrate the importance of early issue intervention—before they have their negative impacts expand. This wisdom’s application to enterprise data quality is clear. given the potential for the effects of bad or anomalous data to ripple outward. Over time, even minor inconsistencies can poison overall data quality, reduce data trust, and diminish end-user adoption of technologies.
Embracing data observability initiatives empowers enterprises to identify and resolve simple glitches and complications that hinder data quality and end-user experience, remedying them as they arise. This reduces the threat that those issues will compound over time. It also means that end users will not end up developing ad-hoc “solutions” (read “hacks”) that lead to bigger, more debilitating, more costly technology failures down the line.
Why is Data Observability Important?
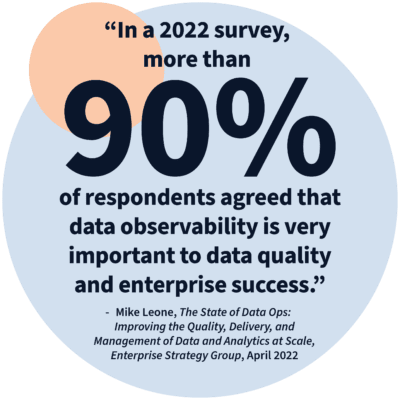
When it comes to enterprise-critical data, data observability practices provide significantly greater visibility into the key issues that can make or break data quality. Those practices help your enterprise to:
1. Bolster data quality
Catching bad data early is essential to preserving data, employee, and customer trust.
2. Monitor data predictability and consistency
Smart enterprises leverage the predictive potential of data. Monitoring its quality helps bolster the accuracy of those predictions.
3. Manage data flow throughout the enterprise data pipeline
Routine monitoring helps to ensure that the right data is available to the right end-users at the right time.
4. Prevent inadvertent use of bad or inaccurate data
Observability initiatives can flag data anomalies at any point in the data lifecycle and prevent them from tainting data quality.
5. Align and map data to suit business needs
Companies committed to observability gain a clearer understanding of how data moves throughout the organization—and take proactive steps to tailor data paths to achieve desired objectives.
6. Maintain effective data governance
Observability can flag—and halt—the unauthorized transmission of sensitive data, allowing for early remediation and reduced risk of compliance violations.
So How Can You Leverage Data Observability in Your Enterprise?
One of the most effective tools for finding and addressing data freshness, distribution, volume, schema, and lineage are Revenue Data Operations platforms. Designed to unify, govern, and distribute siloed revenue and communications data by connecting CRM, email, calendar, contacts, and chat platforms, Revenue Data Operations provide meaningful, real-time data observability functionality.
Take, for example, Riva Insight: a sidebar feature available in two of Riva’s Data Ops toolkits. Insight allows end-users to review customer data in their workflows, in real-time, while providing the opportunity to identify and correct data errors, omissions, and duplications on the fly. Riva’s admin dashboards and tools provide workflows for RevOps and IT to monitor data use at any point during its lifespan. This ensures data consistency by defining and controlling data entry parameters, and to flag and address unauthorized data use.
In effect, Revenue Data Operations solutions provide a gateway to improved data observability by:
- Connecting siloed and/or pooled data
Until it’s connected and channeled into accessible pipelines, revenue and communications data is of little value to the enterprise. Revenue Data Operations form essential connections that pull data from isolation and make it available for use. - Channeling data to observable platforms
By establishing data pipelines to make revenue and communications data available, Revenue Data Operations can improve opportunities for human and machine learning to enhance the platforms end-users rely on—in forms they can use to improve everything from product development to customer relationship development and sales. - Governing data distribution and use
Most Revenue Data Operations solutions offer some level of data governability—allowing administrators to define data objects, control data access, and flag irregular data and data usage.
Conclusion
The next evolution in digital transformation relies heavily on leveraging quality data, and data observability boils down to common sense applied with best practices! The more insight you have into your data, the greater its potential impact on improving end users’ lives and supporting bigger-picture organizational objectives. As an early adopter, you’ll put your enterprise—and your customers—in the best possible position to succeed.
Recent Articles
- What is Agentforce? Salesforce’s AI Agents Explained
- Digital Transformation in Banking: Trends, Challenges, and Future Insights
- Three Key Takeaways from Dreamforce San Francisco 2024
- What is AI Copilot in CRM: Detailed Guide with Examples
- Building a Strong Network of Salesforce Professionals at the Nebraska Summit

